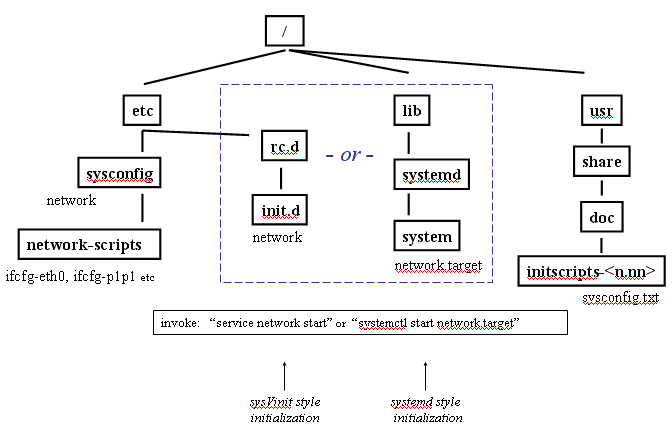
setting up automatic network configuration
You can set up IP configuration manually, running the ifconfig and route
commands yourself. Or you can run a script that will do it for you, if you first
place the needed configuration arguments in strategic files to be picked up by
the script. You can run the script ad hoc at any time, or set it to be auto-run
at boot time in the usual way ( sysVinit or systemd initialization mechanism,
whichever your platform uses). Here is a filesystem map:

The essentials for automating network configuration are to place appropriate content into two files then reboot (or run the initialization without rebooting). The files are:
/etc/sysconfig/network
/etc/sysconfig/network-scripts/ifcfg-eth0 (or other name for your interface, if not eth0)
If you have multiple interfaces, there will be one "ifcfg-<interface name>" file for each. Running the initialization consists of invoking the command shown in the filesystem diagram, depending which initialization mechanism is installed on your computer (actually configuring the files is done identically, independent of init mechanism). Incidentally, the script that processes these files does so by looping across files in this directory. By there mere presence they get swept up in the processing net. So if you save a copy of an "ifcfg-..." file under another name in order to experiment with the original, don't leave the copy in this directory.
The file that documents what to put in the config files is:
/usr/share/doc/initscripts-9.37/sysconfig.txt
Here are excerpts (but see the file itself for full doc):
/etc/sysconfig/network:
NETWORKING=yes|no
HOSTNAME=<fqdn by default, but whatever hostname you want>
Note that this can be overriden by /etc/hostname.
GATEWAY=<gateway IP>
GATEWAYDEV=<gateway device to use, when multiple devices have GATEWAY=> (e.g. eth0)
VLAN=yes|no
NOZEROCONF= # set this one to "no" to avoid dynamic link-local
addresses (169....)
/etc/sysconfig/network-scripts/ifcfg-<interface-name> and
Base items:
DEVICE=<name of physical device (except dynamically-allocated PPP
devices where it is the "logical name")>
IPADDRn=
PREFIXn=
Network prefix. It is used for all configurations except aliases
and ippp devices. It takes precedence over NETMASK when both
PREFIX and NETMASK are set.
NETMASKn=
Subnet mask; just useful for aliases and ippp devices. For all other
configurations, use PREFIX instead.
The "n" is expected to be consecutive positive integers starting from 0.
It can be omitted if there is only one address being configured.
GATEWAY=
ONBOOT=yes|no (not valid for alias devices; use ONPARENT)
BOOTPROTO=none|bootp|dhcp
'bootp' or 'dhcp' cause a DHCP client to run on the device. Any other
value causes any static configuration in the file to be applied.
DNS{1,2}=<ip address>
provide DNS addresses that are dropped into the resolv.conf
file if PEERDNS is not set to "no".
HWADDR=
ethernet hardware address for this device
NM_CONTROLLED=yes|no
If set to 'no', NetworkManager will ignore this connection/device.
Defaults to 'yes'.
For dynamic addressing (BOOTPROTO=dhcp) only DEVICE needs to
be set; all the rest will be determined by the boot protocol.
The exercise to perform:
Operate as root. Identify the name of your main interface:
ifconfig -a
It might be named eth0, or em1, or p2p1, or some such. Note the name. Verify the presence of its corresponding configuration file:
ls /etc/sysconfig/network-scripts/ifcfg-<interface-name>
Save the 2 files you are going to change (to your home directory, outside of /etc/sysconfig/network-scripts):
cp /etc/sysconfig/network ~/network.org
cp
/etc/sysconfig/network-scripts/ifcfg-<interface-name> ~/ifcfg-<interface-name>.org
Edit /etc/sysconfig/network to have the following contents:
NETWORKING="yes"
HOSTNAME="testname"
ONBOOT="yes"
Edit /etc/sysconfig/network-scripts/ifcfg-<interface-name> to have the following contents:
DEVICE="<interface-name>"
ONBOOT="yes'
NM_CONTROLLED="no"
IPADDR="55.66.77.88"
NETMASK="255.255.255.0"
GATEWAY="55.66.77.1"
Reinitialize:
systemctl restart network.service or service network restart
check things out:
ifconfig -a
route -n
(The hostname change will not manifest itself, but would be adopted if you were to do a full reboot.) Now change /etc/sysconfig/network to read:
DEVICE="eth0"
ONBOOT="yes"
NM_CONTROLLED="no"
BOOTPROTO="dhcp"
Reinitialize:
systemctl re start network.service or service network restart
check:
ifconfig -a
route -n
Restore:
cp ~/network.org /etc/sysconfig/network
cp
~/ifcfg-<interface-name>.org /etc/sysconfig/network-scripts/ifcfg-<interface-name>
Reinitialize, back to the original state:
systemctl re start network.service or service network restart