mounting a remote filesystem securely with dokan (sshfs equivalent for Windows)
Windows can import a directory through ssh from a remote linux server machine. That is, the linux machine's directory will appear on the Windows client as a drive letter.
Linux clients do the same thing using the sshfs program. Windows uses the functionally similar 3rd-party program "dokan", which means "clay pipe" in Japanese suggesting the transport and delivery through to Windows of the linux file tree. The remote machine need only run the sshd server (as many do). Provided only you can ssh-authenticate to the linux machine for any purpose (e.g., the usual remote login), you can as well use it for this purpose.
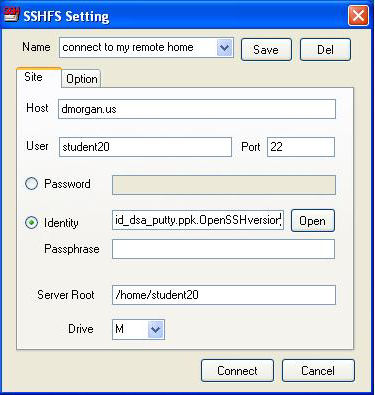
Here is a good guide for installing dokan and the programs that support it. Please install it. Run it. Specify your authentication credentials (user account on the target linux/sshd machine, together with password or private key), and drive letter choice, like this:

Note that this operation depends on the usual in-place pre-established ssh key
relationship between the two users. That is, the logged-in Windows user's
private key being in file id_dsa_putty.ppk.OpenSSHversion, that key's public-key
counterpart must previously have been lodged in /home/student20/.ssh/authorized_keys2
on the linux machine dmorgan.us. Note also that the linux machine,
presumably running the OpenSSH version of ssh, requires the OpenSSH format for
the public key. Should you have used OpenSSH for Windows on the windows side to
generate your keys they will be in that format. Should you have used PuTTY,
which stores both the public and private keys it generates in its own format,
take care to convert it to OpenSSH format (a cut-and-paste operation within
PuTTY). The acid test for all this will have been success at gaining a
password-less ssh login session-- if you can log in, then dokan can fileshare. When it
does, the result looks like this:
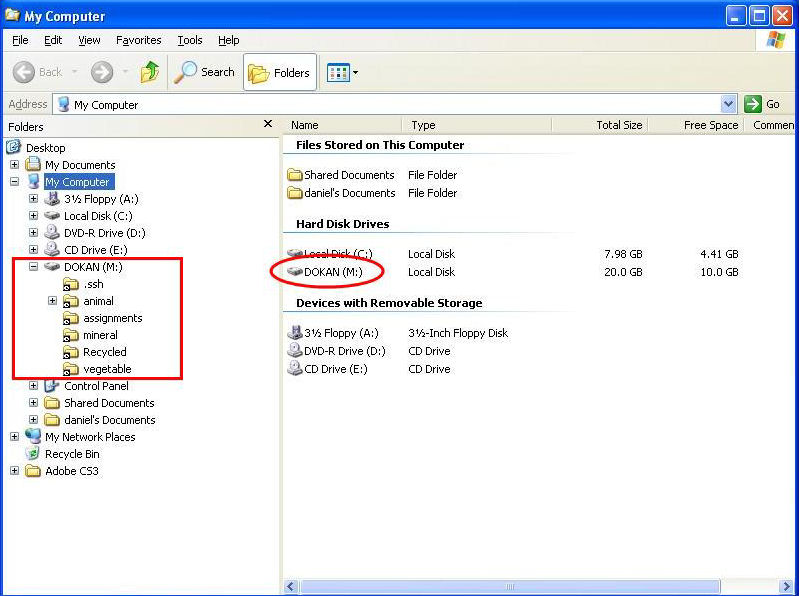
Subject to
permissions by the user as whom you connected (student20 in this case), you are free to use these files
as "your own" on the Windows machine.
The assignment for you to perform
Use an editor in Windows to create a file called with name and contents indicated by your instructor. Save it in the "assignments" subdirectory within your home directory on the linux machine. When done, unmount/unconnect via the "SSH" icon in the system tray (right click on it).